Table of Contents
Understanding Pigmentation: Types and Causes
When it comes to the world of skincare, achieving that radiant complexion isn’t just about fighting acne or preventing wrinkles. Understanding pigmentation, its various types, and the underlying causes can make all the difference in your quest for beautiful, flawless skin. Pigmentation plays a significant role in your skin’s overall appearance, and being well-informed about it is key. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the exciting world of pigmentation, from the different types that affect us to the underlying factors that trigger them.
Discover more about the causes and treatments of hyperpigmentation.
The Melanin Story
At the heart of the pigmentation saga lies melanin. This pigment, produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, determines the color of our skin, eyes, and hair. Your unique skin tone is a result of the quantity and distribution of melanin in your skin. To truly understand pigmentation, we must start with an exploration of melanin.
Hyperpigmentation: The Dark Side of the Spectrum
Hyperpigmentation refers to areas of the skin that become darker than the surrounding skin. It’s a widespread concern and can be triggered by several factors, leading to different types of hyperpigmentation.
1. Sunspots (Solar Lentigines)
Sunspots, also known as solar lentigo or age spots, are a common form of hyperpigmentation. These are small, darkened patches that typically appear on areas of the skin that have been exposed to the sun over the years, such as the face, hands, and shoulders. Prolonged UV exposure stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin, randomly in some areas of the skin, resulting in the formation of these spots. Will usually appear in later ages, from your 40’s. At the age of 60 90% of the population will have some sunspots. Sunspots tend to be worse for men since many of them spend more time outside and less time in the kitchen:) And fewer of them apply sunscreen as they should if at all.

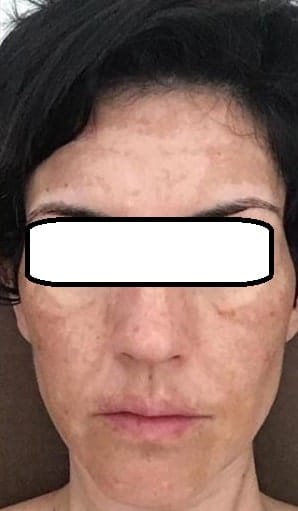
2. Melasma: The Mask of Pregnancy
Melasma, often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy,” is a specific type of hyperpigmentation. It tends to affect pregnant women due to hormonal changes, but it can also occur in individuals taking birth control pills or undergoing hormone replacement therapy. Melasma appears as brown or grayish patches, on the face, specifically chicks, which give it the butterfly shape, but not limited to the chicks. It can appear on the forehead too and sometimes all over the face. Melasma affects women from a very young age and causes stress and low self-esteem issues. Even though women’s hormones change all the time Melasma has a tendency to stay and not disappear long after it first appears. It does fade with menopause sometimes but not always.
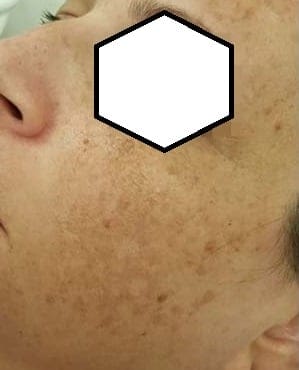
3. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is another common form of hyperpigmentation. It occurs as a result of skin trauma or inflammation, often following conditions like acne, rashes, or injuries. When the skin is inflamed or damaged, melanocytes can become overactive, leading to the darkening of affected areas. It’s important to understand that post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation can be caused by many things: Dry skin, sensitivity to skincare ingredients, sunburn, heat – sometimes even a hot shower can trigger it and make it worse, even the touch of the hair – can cause pigmentation along the chin line. As we age, the skin is less forgiving, this is why young girls have flawless skin even though they do all of the above. At a later age, this does not work anymore and you should be mindful about how you treat your skin.
Hypopigmentation: A Lighter Shade of Complexity
Hypopigmentation, in contrast to hyperpigmentation, is characterized by areas of skin that are lighter than the surrounding skin. While less common than hyperpigmentation, it’s essential to understand this condition, as it can also affect your skin’s appearance and sometimes can be perceived as hyperpigmentation.
1. Vitiligo: The Loss of Pigment
Vitiligo is a well-known example of hypopigmentation. It’s an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys melanocytes. This results in the formation of white patches on the skin. Vitiligo can have a profound impact on one’s self-esteem and quality of life.

Photo by Inna Kapturevska_Ua
2. Tinea versicolor: Sun fungus
This skin condition looks a lot like melasma but will usually start in the neck, upper back, and shoulders, and if left untreated can spread to the face. Usually, the doctor will prescribe antifungals for this condition but it might be misdiagnosed as vitiligo.
Freckles and Birth Marks
Freckles and birthmarks are concentrated areas of pigmentation that often catch our attention due to their distinct appearance.
1. Freckles: Nature’s Unique Markers
Freckles are typically hereditary and more commonly found in individuals with fair skin. They tend to darken upon sun exposure and lighten during periods of reduced sun exposure. Freckles are generally harmless and can add character to an individual’s appearance. Some people do not like them though and the good news are that they are easy to treat because of their seasonal/changing character.
2. Pigmented Birthmarks: An Abundance of Pigment Cells
Pigmented birthmarks are caused by an overabundance of pigment cells in certain areas of the skin. Examples include café-au-lait spots and Mongolian spots. Many times left untreated unless if appears on the face.
Unmasking the Culprits: Causes of Pigmentation Issues
To effectively manage and prevent pigmentation problems, understanding their underlying causes is crucial. Several factors can trigger these skin concerns.
1. Sun Exposure: The Leading Cause
One of the primary culprits behind pigmentation issues is sun exposure. UV radiation from the sun can stimulate melanocytes to produce more melanin as a protective measure against UV damage. While this is a natural defense mechanism, it can lead to the development of hyperpigmentation, especially in individuals with lighter skin tones. It’s important to bear in mind that any pigmentation will become darker when exposed to the sun and make it darker so sun protection is very important even if your pigmentation is hormonal or Post-inflammatory.
2. Hormonal Changes: The Melasma Connection
Hormonal fluctuations can play a significant role in triggering pigmentation issues. For example, melasma is often associated with pregnancy due to hormonal changes during this period. However, it can also occur in women taking birth control pills or undergoing hormone replacement therapy. These hormonal shifts can lead to an increase in melanin production and the appearance of melasma.
3. Inflammation and Trauma: Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Inflammatory skin conditions, such as acne, can leave behind post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). When the skin experiences inflammation or trauma, melanocytes may become overactive, resulting in the darkening of affected areas. Here we can find also drug-induced pigmentation. Yes, drugs you take, like antibiotics and painkillers can start the process of hyperactive melanocytes. Trauma does not have to be very dramatic. If your skin is susceptive to pigmentation it can be one time you’ve got sunburnt or even sauna. Ideally, you pay attention to these causes and know your triggers.
4. Genetics: The Family Connection
Genetics also play a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to certain pigmentation issues, especially melasma. If your mom has melasma and so do all of your aunties, you may be more likely to develop them as well. Also, women of color have a greater tendency to get hyperpigmentation. (But white people get more wrinkles!:)
Empower Yourself with Knowledge
Understanding the types and causes of pigmentation is the first step toward achieving healthier and more radiant skin. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions about your skincare routine, sun protection, and the selection of treatments tailored to address specific pigmentation concerns. Saying this, you can’t always know the exact reason for your pigmentation. You may know, or assume how it started but it’s usually a combination of causes. Some of them, like heredity, you can’t change but if you can avoid the cause, like say sun exposure, by all means, do that. Y’ll see faster results for longer this way.
The Path Forward: Your Journey to Beautiful, Radiant Skin
In the coming weeks, we’ll dive deeper into the world of pigmentation care, exploring natural remedies, effective skincare products, and advanced, expensive treatments. I, of course, recommend my products because I think it’s the fastest, safest, cost-effective way to go but our goal is to provide you with all of the knowledge you need in order to make a well-informed decision.
Whether you’re looking to fade stubborn sunspots, lighten melasma, or simply enhance your overall skin tone, we’ve got you covered. Stay tuned for future articles that will equip you with the tools and knowledge to unveil your skin’s natural radiance. Your journey to flawless, pigmentation-free skin starts here!
In the meantime, remember that understanding pigmentation is a powerful step toward achieving the skin you’ve always dreamed of. It’s a journey, but with the right knowledge and approach, you can embrace your skin’s unique beauty and keep it looking its best.



Excellent blig! Very informative, very useful. Looking forward to using your products.
Thank you Betsy, posted last week. Hope you’ll get it soon. You won’t regret. Cheers!